Similar
Post-mortem pathology; a manual of post-mortem examinations and the interpretations to be drawn therefrom; a practical treatise for students and practitioners (1905) (14597903200)
Summary
Identifier: postmortempatho00catt (find matches)
Title: Post-mortem pathology; a manual of post-mortem examinations and the interpretations to be drawn therefrom; a practical treatise for students and practitioners
Year: 1905 (1900s)
Authors: Cattell, Henry Ware, 1862-1936. (from old catalog)
Subjects: Anatomy, Pathological Autopsy
Publisher: Philadelphia and London, J. B. Lippincott company
Contributing Library: The Library of Congress
Digitizing Sponsor: The Library of Congress
Text Appearing Before Image:
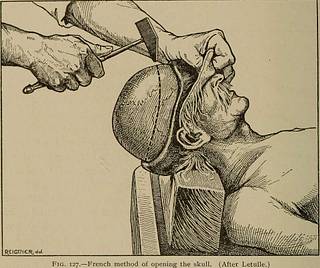
posterior to the apex of the ear. Alwaystry to saw above the line of the hair in front. Although this makesthe anterior fossa deeper and consequently the removal of the brainmore difficult, it obviates the ugly ridge on the brow so liable to bemade by the inexperienced. It is necessary too that the angles be wellsawed through and carefully broken, because if spicules of bone remainthe brain may be caught and injured during its removal. (For thismethod of opening see Figs. 123 to 126 inclusive.) 228 POST-MORTEM EXAMINATIONS In the French method of opening the adult skull with a hammer,1the anterior and posterior flaps are made in the usual manner. A lineone centimetre above the soft tissue is drawn around the skull with asoft pencil or with ink, the temporal muscles being cut through with aknife; by means of blows with the hammer the skull is then fracturedalong this line. The sound tells you when the bone is fractured andwarns you to proceed to a new place. (Fig. 127.) This method is
Text Appearing After Image:
(After Letulle.) much employed in France, and in the hands of experienced operatorsgives good results, though it is most difficult of performing in the re-gion of the exterior occipital protuberance. It must not be used inchildren, in cases of fractures, bone lesions, etc. The dura is openedalong the circular incision, or, more frequently, crucial incisions aremade on either side of the longitudinal sinus and each side is incisedby a perpendicular cut running from the vertex down to the upper mar-gin of the bone. The four pieces are then turned down and the falxcerebri is cut anteriorly just behind the crista galli and with a portion 1 J. Dejerine, Anatomie des centres nerveux, 1895, p. 13. EXAMINATION OF THE SKULL AND BRAIN 229 of dura on each side of the longitudinal sinus pulled backward. Itwill be seen that the dura mater thus covers the sawed portions ofthe bones (Fig. 128) and affords a protection to the hands in thesubsequent removal of the brain. Aseptic compresses may also be
Tags
Date
Source
Copyright info




















