Similar
Harmonia macrocosmica, seu, Atlas universalis et novus, totius universi creati cosmographiam generalem, et novam exhibens : in quâ omnium totius mundi orbium harmonica constructio, secundum diversas diversorum authorum opioniones, ut et uranometria seu totus orbis coelestis, ac planetarum theoriae, et terrestris globus, tàm planis et scenographicis iconibus, quàm descriptionibus novis ab oculos ponuntur : opus novum, antehac nunquam visum, cujuscunque conditionis hominibus utilissimum, jucundissimum, maximè necessarium, & adornatum /
Summary
Public domain scan of a page from geographical atlas, geography, free to use, no copyright restrictions image - Picryl description
Approximately 2000 B.C., Babylonian astrologers believed that the Sun, Moon, and the five planets known at that time (Jupiter, Mars, Mercury, Saturn, and Venus) possessed distinct powers. Mars, for example, appeared to be red and was associated with aggression and war. Astrology was inherited by the Greeks from Babylonians around the 4th century B.C.Through the studies of Plato, Aristotle, and others, astrology came to be regarded as a science. It was embraced by the Romans and the Arabs. The zodiac (which is derived from the Greek word meaning "circle of animals") is believed to have developed in ancient Egypt and later adopted by the Babylonians. Early astrologers knew it took 12 lunar cycles (i.e., months) for the sun to return to its original position. They then identified 12 constellations that they observed were linked to the progression of the seasons and assigned them names of certain animals and persons (in Babylonia, for example, the rainy season was found to occur when the Sun was in a particular constellation which was then named Aquarius, or water bearer). Each of these four groups is inscribed in its own quadrant, or group of "houses," on a circle. The division of the 12 houses is based on Earth's daily rotation and relates to such circumstances as relationships, finances, travel, etc. The division of the 12 signs of the zodiac is based on the earth's year-long rotation around the Sun and relates to character traits and areas of life.
Rennaisance Cosmography, Astronomy, and Astrology Images and Diagrams
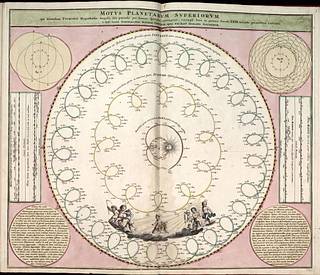
Harmonia Macrocosmica. Amsterdam 1708. Harmonica Macrocosmica consists of 29 double plates made in sumptuous baroque style. The first part describes cosmological theories, as well as illustrates motions of the sun and planets that were discovered by Ptolemy, Copernicus, and Tycho Brahe. The last eight plates depict constellations of both celestial hemispheres and planispheres. These ones have a high level of artistic detail and are considered very precious by the collectors of fine arts. Cellarius’s atlas is the seventh volume of a complex work started by Gerardus Mercator a century earlier. His idea was to publish an atlas that will cover everything known about cosmos, as well as geography, and history of the earth. He composed five volumes and the sixth one was finished by his son, Rumold. The collection includes digitized plates of the famous atlas and are provided by the Library of Congress.
Collection - Astrology
Astrological Images found in ancient manuscripts and printed books.Collection - Astronomy and Astrology
Cosmography, Astronomy, and Astrology Images and DiagramsCollection - Harmonia Macrocosmica 1708.
Star atlas was written in 1660 by Dutch-German mathematician and cosmographer Andreas Cellarius and covers everything about the sky dome known by that time.
Tags
Date
Contributors
Source
Copyright info



































































































